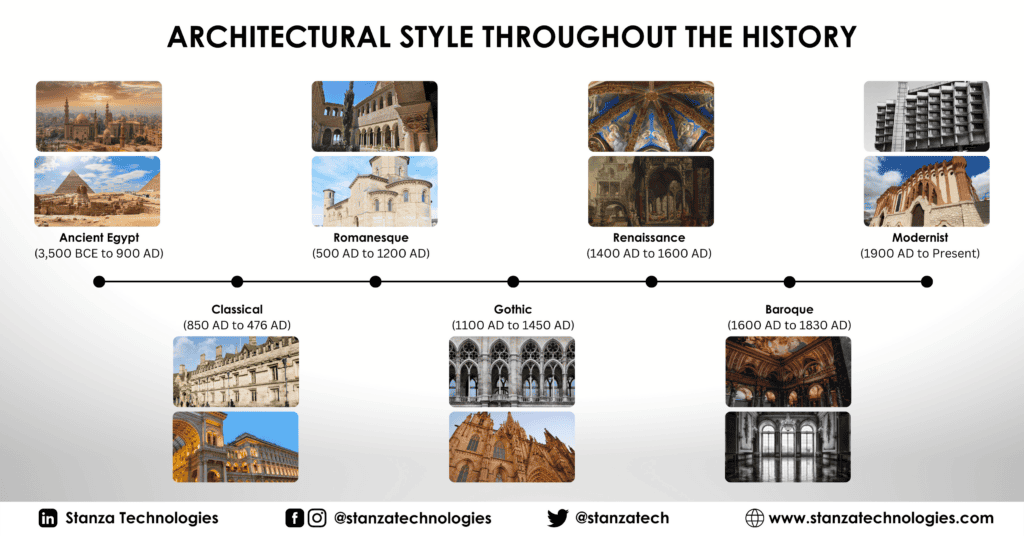
The progress of architectural designs has represented the evolution of humanity. Showing various styles based on different aspects such as belief, religion, fashion, and technology. Discover the distinct architectural styles and their development from Antiquity to the Present Day.
- Ancient Egypt – (3,500 BCE to 900 AD) produced architectural monuments during the dynastic period. Aimed to preserve forms and conventions reflecting the perfection of the world at the primordial moment of creation.
- Classical – (850 AD to 476 AD) consciously derived from the principles of Greek and Roman classical antiquity. Most often defined by the designs and ornamentations of columns and pediments.
- Romanesque – (500 AD to 1200 AD) Based on the Roman architecture design, characterized by round arches, massive stones, and a propensity for housing art and sculptures.
- Gothic – (1100 AD to 1450 AD) was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century. Characterized by cavernous spaces with the expanse of the wall broken up by overlaid tracery.
- Renaissance – (1400 AD to 1600 AD) reflected the rebirth of Classical culture that originated in Florence. Characterized by the use of classical orders and mathematically precise ratios of height and width combined with symmetry, proportion, and harmony.
- Baroque – (1600 AD to 1830 AD) highly opulent style of building, design, and art. Characterized by extremely detailed forms, marble, large-scale decoration, and bright colors.
- Modernist – (1900 AD to Present) associated with the function of buildings, approached from an analytical viewpoint, rational use of materials, the elimination of ornament and decoration, and openness to structural innovation.
- Post-modernist – (1972 AD to Present) is an international movement focused on free-thinking design with conceptual consideration of the surrounding environment. Re-invented historical details and ideas dated back to classical and ancient times.